Pay transparency legislation has rapidly expanded across the United States, creating a complex compliance landscape that fundamentally impacts business operations, employer practices, and HR strategic planning. With over 15 states and numerous municipalities implementing comprehensive pay disclosure requirements, organizations must navigate varying legal frameworks while maintaining competitive positioning and operational efficiency. This article examines the current legislative landscape and provides strategic guidance for HR teams managing multi-jurisdictional compliance requirements.
Current State Legislative Landscape
Comprehensive Pay Transparency States
California leads with extensive requirements under SB 1162, mandating salary ranges in job postings for employers with 15+ employees and annual pay data reporting for companies with 100+ employees. The law applies to remote positions that could be performed in California, creating broad jurisdictional reach.
New York implemented statewide pay transparency requirements in 2023, requiring salary ranges in job advertisements and extending beyond New York City’s earlier municipal ordinance. The law covers all employers with four or more employees.
Colorado pioneered comprehensive pay transparency with requirements for salary ranges in job postings, benefits information, and advancement opportunities. The law applies to all positions that could be performed in Colorado, including remote work.
Washington requires salary disclosure for positions with 15+ employees, with specific provisions for remote work and multi-state employers. The law includes penalties for non-compliance ranging from civil violations to private lawsuits.
New Jersey requires employers to disclose salary or wage ranges in job postings, including internal postings for promotions and transfers. This applies to jobs advertised both externally and internally.
Emerging Legislative States
Connecticut, Maryland, Nevada, and Rhode Island have enacted varying forms of pay transparency requirements, from salary range disclosure upon request to mandatory posting requirements. Each state presents unique compliance considerations and penalty structures.
Illinois, Massachusetts, and Minnesota have pending or recently enacted legislation with implementation timelines extending into 2024-2025, requiring proactive preparation by employers.
Business Impact and Operational Challenges
Multi-State Compliance Complexity
Organizations operating across multiple states face significant compliance challenges as laws vary substantially in scope, coverage thresholds, and enforcement mechanisms. Companies must develop sophisticated systems to track varying requirements across jurisdictions while maintaining consistent internal practices.
Competitive Positioning Concerns
Pay transparency forces employers to weigh how much compensation information they reveal while staying competitive in attracting talent. Organizations report increased difficulty maintaining salary confidentiality while competitors gain visibility into compensation strategies.
Administrative Burden and Costs
Compliance implementation requires substantial administrative investment, with organizations reporting 25-40% increases in HR administrative workload related to job posting management, salary range development, and reporting obligations.
HR Team Planning Process Transformation
Policy Development and Standardization
HR teams must develop comprehensive policies addressing pay transparency requirements across all applicable jurisdictions. This includes establishing consistent salary range methodologies, approval processes, and communication protocols that satisfy varying legal requirements.
Technology Infrastructure Requirements
Modern HRIS systems require upgrades to support automated compliance tracking, multi-state job posting management, and reporting capabilities. Organizations investing in compliance technology report 60% reduction in manual compliance workload.
Training and Change Management
HR teams require extensive training on varying state requirements, legal interpretation, and operational procedures. This includes manager training on salary discussions, recruiter education on disclosure requirements, and legal compliance protocols.
Compliance and Reporting Imperatives
Automated Compliance Monitoring
Organizations must implement systems to track compliance across multiple jurisdictions automatically. Failure to maintain current compliance can result in penalties ranging from $300-$15,000 per violation, depending on jurisdiction. Of note, there are easily accessible software applications designed for HR teams which streamline this process of not only creating and managing pay transparency operations, and also provides immediate access for all reporting requirements.
Pay Data Reporting Requirements
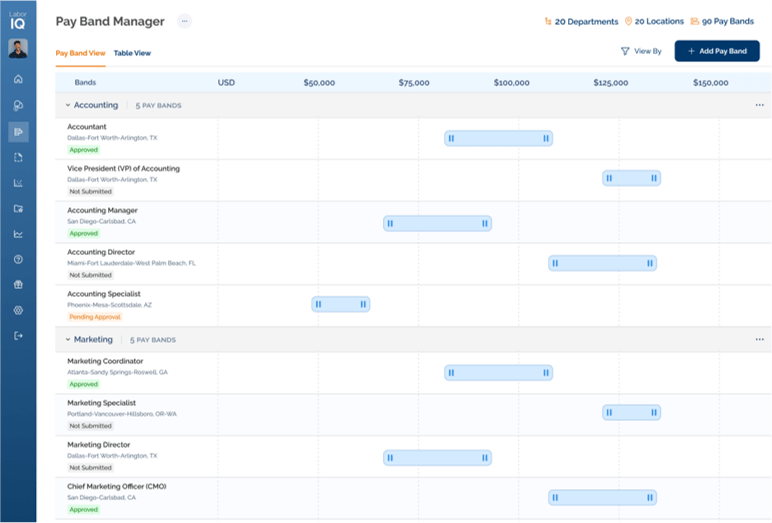
States like California require annual pay data reporting with detailed demographic breakdowns, necessitating sophisticated data collection and analysis capabilities. Organizations must prepare for increased regulatory scrutiny and potential investigations. LaborIQ’s Pay Band Manager and Pay Analysis solutions tools help HR teams benchmark salaries and meet pay equity reporting requirements with downloadable, editable documentation.
Audit Preparation and Documentation
Proactive audit preparation becomes essential as enforcement agencies increase investigation activities. HR teams must maintain comprehensive documentation of salary determination processes, pay equity analyses, and compliance efforts.
Operational Preparedness Strategies
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful compliance requires coordination between HR, Legal, Finance, and IT departments. Organizations establishing cross-functional compliance teams report 50% fewer compliance issues and faster adaptation to regulatory changes. LaborIQ’s software allows HR teams to share views, send pay bands for approval, or quickly share organizational views to all key stakeholders in their organization.
Vendor and Technology Selection
Selecting compliance-capable vendors for HRIS, job posting platforms, and compensation management becomes critical. Organizations should evaluate vendor capabilities for multi-state compliance tracking and automated reporting.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates
Pay transparency laws continue evolving, requiring continuous monitoring of legislative changes and regulatory guidance. Organizations must establish processes for rapid policy updates and implementation adjustments. And with LaborIQ, pay band creation, approval dates, and automating update flows are done for the user, making it simple to implement reporting compliance.
Strategic Recommendations
Proactive Compliance Approach
HR leaders should go beyond basic legal compliance by adopting robust pay transparency practices. This strengthens compliance, boosts operational efficiency, and supports smarter HR decision-making.
Investment in Technology Infrastructure
Strategic technology investments in compliance management, automated reporting, and integrated HRIS systems deliver long-term operational benefits that justify initial implementation costs.
Legal and Consulting Partnership
Engaging specialized legal counsel and compensation consultants provides essential expertise for navigating complex regulatory requirements and developing sustainable compliance strategies.
Conclusion
U.S. pay transparency laws represent a fundamental shift in employment practices that requires strategic organizational response. HR teams must prioritize operational preparedness through comprehensive policy development, technology infrastructure investment, and proactive compliance management. Organizations that embrace transparent compensation practices while maintaining robust compliance frameworks will achieve competitive advantage in talent attraction and retention while minimizing legal risk in an increasingly regulated environment.
Sources for this article include:
- U.S. Department of Labor guidance and resources
- State bar associations’ employment law sections
- HR compliance consulting firms’ research and analysis