Effective compensation strategy requires precise calibration across three fundamental dimensions: geographic location, professional experience, and job title complexity. Failing to adjust compensation for location, experience, and job title can hinder talent acquisition, increase turnover, and weaken competitiveness in a fast-moving labor market. This white paper examines the strategic importance of multi-dimensional pay setting and provides HR professionals with data-driven approaches to optimize compensation practices.
The Geographic Pay Imperative
Market Reality and Cost Variations
Geographic location represents the most significant variable in U.S. compensation structures, with salary differences exceeding 40% between major metropolitan areas. Software engineers in San Francisco command median salaries of $165,000, while similar roles in Atlanta average $115,000, reflecting substantial cost-of-living and market competition variations.
Remote Work Complications
The rise of remote work has complicated location-based pay strategies, with 42% of organizations now employing workers across multiple states. Companies must navigate varying minimum wage laws, overtime regulations, and pay transparency requirements while maintaining internal equity and competitive positioning.
Experience-Based Compensation Modeling
Career Progression Analytics
Professional experience directly correlates with compensation levels, typically following predictable progression curves. Entry-level positions average 15-25% below market midpoints, while professionals with 10+ years of experience command 20-35% premiums. However, experience valuations vary significantly by industry and role complexity.
Skills Premium Calculation
Organizations increasingly recognize that experience quality matters more than tenure alone. Specialized skills, certifications, and demonstrable achievements create compensation premiums that can exceed traditional experience-based increases by 10-20%.
Job Title Complexity and Market Positioning
Title Inflation Challenges
Job title inflation has created market distortions, with identical responsibilities carrying different titles and compensation levels across organizations. HR professionals must focus on role complexity, scope, and impact rather than relying solely on title matching for pay decisions.
Hierarchical Pay Structures
Effective pay structures maintain logical progressions between job levels, typically requiring 15-25% salary increases for promotions. Organizations with compressed pay bands experience higher turnover as employees seek advancement opportunities elsewhere.
HR-Focused Implementation Strategies
Multi-Dimensional Data Integration
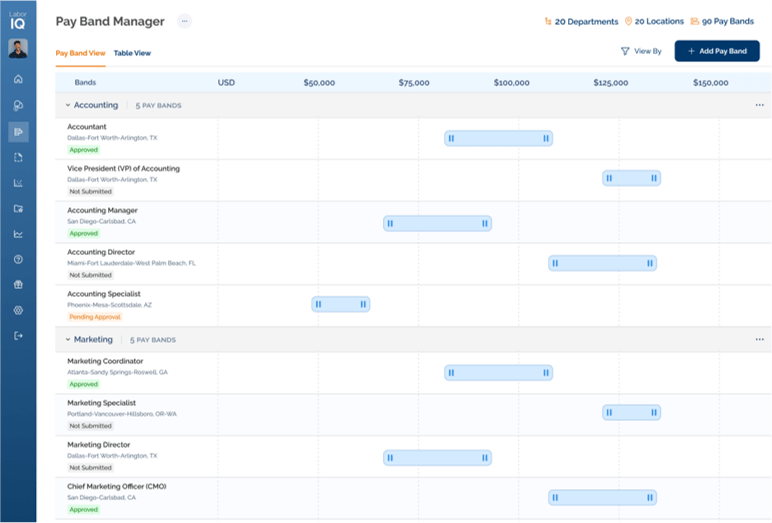
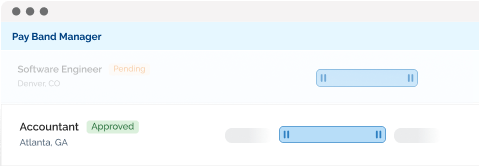
Effective compensation management requires integrated salary benchmarking across location, experience, and role complexity—functions built into platforms like LaborIQ. LaborIQ along with other platforms like Radford, Mercer, and PayScale create comprehensive compensation models that account for multiple variables simultaneously.
Recommended Data Sources:
- LaborIQ for real-time salary recommendations
- Compensation consulting firms for comprehensive market analysis
Geographic Pay Policies
Establish clear policies for location-based pay adjustments, including:
- Cost-of-living adjustment methodologies
- Remote work compensation frameworks
- Relocation pay adjustment procedures
- Multi-state compliance protocols
Experience Valuation Frameworks
Develop structured approaches to experience assessment:
- Skills-based competency models
- Performance-weighted experience calculations
- Industry-specific experience premiums
- Certification and education multipliers
Hiring Strategy Optimization
Competitive Positioning
Organizations using comprehensive pay data gain significant advantages in talent acquisition. Companies with location-adjusted, experience-calibrated compensation offers achieve 35% higher acceptance rates and reduce negotiation cycles by an average of 40%.
Candidate Communication
Transparent communication around compensation strategy—including how pay bands are set—builds candidate trust and reduces offer declines. Explain how location, experience, and role complexity influence compensation decisions to demonstrate fairness and market awareness.
Technology and Analytics Integration
Compensation Management Systems
Deploy platforms that automatically adjust pay recommendations based on location, experience, and job complexity variables. Systems such as LaborIQ, enable consistent decision-making while reducing administrative burden and potential bias.
Predictive Analytics
Utilize machine learning algorithms to predict optimal compensation packages based on candidate profiles, market conditions, and organizational constraints. This approach improves offer success rates while maintaining budget discipline.
Measuring Success and ROI
Track key performance indicators including:
- Offer acceptance rates by location and experience level
- Time-to-fill positions across different markets
- Internal pay equity metrics
- Turnover rates by compensation percentile
- Candidate satisfaction with compensation discussions
Strategic pay setting requires sophisticated analysis of location, experience, and job title variables to create competitive, equitable compensation structures. Organizations that master multi-dimensional pay modeling gain significant advantages in talent acquisition, retention, and overall workforce effectiveness. HR professionals must leverage comprehensive data sources, implement robust analytical frameworks, and maintain transparency in compensation decisions to succeed in today’s complex labor market.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)
- LaborIQ Modern Compensation Software (laboriq.co)
- Society for Human Resource Management (shrm.org)
- Compensation consulting firms like Willis Towers Watson, Mercer, and Radford
- Industry salary surveys and reports
- Academic research from business schools and labor economics departments